- LABORATORY
- From autonomous driving to metaverse
본문영역
From autonomous to metaverse,
the power of high-dimensional 3D reconstruction,
which deduces implicit connections with the environment
Professor Kyungdon Joo’s Laboratory
in the UNIST Graduate School of AI
To fulfill or realize autonomous driving, 3D printing, AR·VR, and the latest blockbuster Metaverse, it is important to obtain accurate 3D information. Research in deep-learning-based computer vision has shown the trend of greater precision in 3D recovery technology. Professor Chu Kyung-Don and his research team at the Graduate School of AI have moved one more step forward to predict the scene with the implicit relation between environment and each object as well as the environment that is not exposed, by the expansion of a partial video through the realization of scene graph.
- Story by Editorial Room Photo by Kim Beom-Ki

3D reconstruction of indoor environments, utilizing scene graph
The 3D recovery technology in the field of computer vision has made many accomplishments around the researches that recover the 3D structure from 2-dimensional video and use actual video to obtain the characteristic of an object directly. Especially, these researches have had the goal to recover or recognize the structure of actual environment or the shape of an object in the previous robotic vision or a machine vision system. Especially, the recent emergence of deep learning technique has solved the problems of time, cost and precision that were pointed out as the technical limitations on the 3D recovery of previous computer vision. The deep learning technique has been utilized beneficially for the navigation of autonomous driving, object recognition or remote motion detection and also for the areas of robotics, aviation and national defense. Professor Chu Kyung-Don and his research team in the Graduate School of AI have been focusing on researches in the core field of autonomous driving in the era of the 4th Industrial Revolution, 3D recovery and recognition in close relation to AR and VR, and the convergence of sensors. Among the fields of computer vision, Professor Chu Kyung-Don is specialized in the field of 3D vision and robot vision. Especially, he has been working on the 3D recovery of indoor environments. Like the indoor environment that can be expressed with a rectangular model, they have conducted research into diverse aspects of the recognition of directional data necessary to realize the man-made environment efficiently. The indoor environment has a structural characteristic so that it is possible to express 3D graphing that is based on the important two-dimensional characteristic. “We have made considerable progress with a research project on developing an efficient two-dimensional model for the living space. If the indoor environment is acquired with a dot, we can express the area with several millions of dots. In fact, a human can understand the environment through the expression of a few two-dimensional MINI INTERVIEWS. We have simplified the spatial images composed of countless dots to make lighter images.”
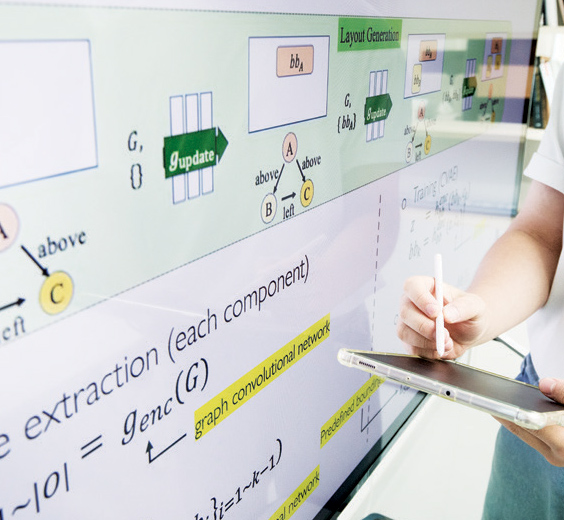
If 3D recovery remains at this stage, it will confront another limitation. It will be equipped to express the structural characteristic of an indoor environment but confront the limitation that prevents it from expressing the actual relation between objects or between an object and the structure of the indoor environment. In order to utilize the 3D recovery to the application of computer vision, a more efficient and articulate expression method is needed. At this time, a scene graph is utilized beneficially. The scene graph has a graphic structure that can show the relation between objects in the scene, which includes both semantic information and physical spatial information.
From parts to an invisible area, expansion and completion of 3D scene graph
The remarkable aspect of the present research by the research team of Chu Kyung-Don is not just a simple physical meaning of an independent two-dimensional model but a high-dimensional model that demonstrates the correlation between two-dimensional surfaces as well as the semantic information by using graphic structure. If it is possible to express the 3D indoor environment in real-time from the video that includes spatial and semantic relation with objects in the indoor environment, it will be feasible to expand and complete the partially observed scene graph to an invisible area by using the structural characteristics of the indoor environment. If we ask a robot to find a pencil, the robot can recognize the relation between the pencil and a desk and move quickly in a direction toward the desk. We have the goal to secure such original technology”
Also, when we develop further to the next stage, it will be possible to recognize a human’s action and location by considering the mutual reaction between a high-dimensional model and the human. It will be an important research development connected to AR·VR and Metaverse. Professor Chu Kyung-Don said, “It is yet followed with no less difficulty compared to the challenges we faced in proceeding with the early stages of research.” There aren’t many researchers who proceed with the 3D recovery research in Korea but there are also many cases of lack of data necessary for learning as there have been few precedent researches in the academic sphere. In this case, to implement the research efficiently, ideas are verified through similar previously existing data to acquire the necessary data afterward.
Led by professor Chu Kyung-Don, the joint research team expects that the present research will create a significant ripple effect on industry and society. First of all, it is possible to resolve the problems of insufficient memory or cost by compressing the scene graph that maintains the spatial and semantic relations with the indoor scene. The 3D expression of indoor environment is combined with the VR that is one of core technologies in the era of 4th Industrial Revolution to utilize it for various fields of medical treatment and education. Also, it is expected to have an impact on robotics-related fields in applications such as robot navigation after predicting the scene from partially observed data.

 MINI INTERVIEW
MINI INTERVIEW
-
-

- Professor Kyungdon Joo
-
-
- “Continue to pursue challenge in new research like the expansion of scene graph”
- Q. How have you been operating the laboratory for better research performance? The process to retain professionality is a continuous challenge in several aspects. To go through such difficulty and obtain better performance, I believe that it is important to have self-motivation. We have made an effort to select and strive for the research theme that each researcher desires by himself in a free and horizontal atmosphere to the extent possible. We try to encourage each researcher to think proactively rather than suggest the details of the theme. We simply provide feedback regarding the macroscopic direction to move forward.
- Q. What are the research projects you are planning and what kind of researcher do you want to remain? The present researches like autonomous driving and AR·VR should be meaningful ones. Its representative research is either the recognition of an object under the road environment or the estimation of depth information. Including such researches, I plan to initiate new researches that have not been handled before by combining various majors such as electronics, robotics and computer, etc. that I have experienced. The expansion of scene graph is one of the ongoing researches. And I want to remain as a researcher who learns and grows continuously even if it takes long years. Moreover, I hope that all members of the research team including me will grow as researchers with both professionalism and the right personality.



